ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis) is like the superhero of the behavior world, swooping in to save the day one reinforced behavior at a time. With its principles intricately woven into the fabric of everyday life, ABA offers a unique toolkit for understanding and modifying behaviors, be it in the classroom or at home. It’s not just about throwing rewards and consequences around; it’s a sophisticated dance of strategies that can lead to genuine transformations.
From boosting communication skills in individuals with autism to creating healthier lifestyles, ABA proves it can adapt to any challenge, making it a jack-of-all-trades in the realm of therapy. Ready to dive into the multi-faceted universe of ABA? Strap on your behavior-analysis goggles, and let’s explore how this powerful technique makes waves in various settings!
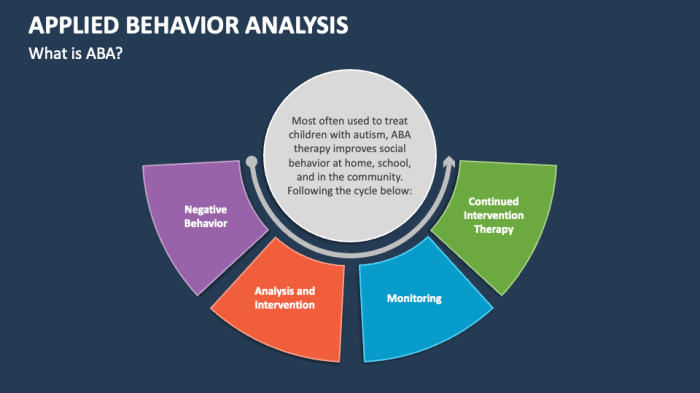
Understanding ABA Principles
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is like the superhero of behavioral science, swooping in to save the day with its powerful toolkit for understanding and modifying behavior. At its core, ABA is built on the idea that behavior is learned and can be changed with the right strategies. It involves a meticulous analysis of how behaviors occur and how they can be influenced, making it a vital approach for helping individuals with autism and other behavioral challenges lead happier and more productive lives.
Understanding the fundamental principles of ABA is essential for implementing effective behavior modification strategies. The most critical components include reinforcement, punishment, and the three-term contingency model: antecedent, behavior, and consequence. These principles not only help us understand why certain behaviors occur but also aid in creating structured environments where positive behaviors can flourish while reducing unwanted ones.
Key Techniques in ABA
The techniques utilized in ABA are particularly fascinating, as they are grounded in scientific principles and yield measurable results. These methods emphasize both reinforcement and punishment, each playing a unique role in shaping behavior. Reinforcement can be positive or negative. Positive reinforcement adds a pleasant stimulus following a behavior, making it more likely to occur in the future. For example, giving a child a sticker after they complete their homework encourages them to continue working hard.
Negative reinforcement, on the other hand, involves the removal of an unpleasant stimulus, like allowing a child to skip chores after they finish their schoolwork. Punishment, conversely, aims to decrease undesired behaviors. It can also be positive (adding an unpleasant consequence) or negative (removing a pleasant stimulus). For instance, if a child throws a tantrum in a store and is denied a toy they wanted, this is a form of positive punishment.
However, if a child loses screen time for not following bedtime rules, that’s negative punishment.
Applications of ABA in Various Settings
ABA principles can be applied in numerous settings, each tailoring techniques to fit specific needs. In schools, educators can use ABA to reinforce positive behaviors, such as paying attention in class. This might involve a reward system where students receive points for good behavior that they can trade for extra recess time. At home, parents might apply ABA by using a token economy.
For instance, children can earn tokens for chores completed or good behavior, which they can exchange for privileges like extra TV time. In therapeutic settings, trainers might focus on teaching social skills through role-playing scenarios where positive interactions are reinforced. For example, if a child successfully interacts with a peer, they might receive verbal praise or a small reward, reinforcing that behavior for future situations.
Important Concepts in ABA
A few key concepts help to ground ABA in science and effectiveness. These concepts include:
-
Observation: Careful observation is essential for understanding the antecedents and consequences that drive behavior.
-
Data Collection: Recording data is paramount in ABA to track progress and adjust strategies as necessary.
-
Individualization: Each person’s program should be tailored to their unique needs, strengths, and preferences.
-
Consistency: Consistent application of strategies ensures behaviors are shaped and maintained effectively.
-
Collaboration: Involving teachers, parents, and therapists creates a comprehensive support system for the individual.
The beauty of ABA lies in its versatility and practicality, empowering individuals to make significant changes in their behaviors, whether in classrooms, at home, or within therapeutic environments.
ABA’s Impact on Developmental Disabilities
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) has become a beacon of hope for individuals with autism and various developmental disabilities, illuminating pathways toward enhanced communication, social skills, and overall quality of life. This evidence-based approach tailors interventions to meet the unique needs of each individual, employing techniques that reinforce positive behaviors while minimizing those that are detrimental. With a sprinkle of humor and a dash of creativity, let’s delve into the transformative power of ABA!
Utilization of ABA in Supporting Individuals with Autism
ABA operates on the belief that every behavior can be understood, taught, and improved, much like a puppy learning to fetch a stick—only with fewer tail wags and more data collection! For individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities, ABA is utilized to foster skill development across various domains. The following highlights key areas where ABA significantly contributes:
- Communication Skills: Utilizing methods such as discrete trial training (DTT), practitioners break down complex language skills into manageable parts, making learning as easy as pie—if pie were a series of rewarding interactions, that is!
- Social Skills: Through role-playing and social stories, ABA helps individuals navigate the often-treacherous waters of social interactions, ensuring they can sail smoothly through conversations—while avoiding icebergs of misunderstanding.
- Daily Living Skills: From brushing teeth to tying shoelaces, ABA teaches essential life skills, making independence a reachable goal, like that cookie jar on the top shelf that requires a step stool—and maybe some ingenuity!
Success Stories Demonstrating ABA’s Effectiveness
When it comes to success stories, the world of ABA is brimming with heartwarming tales and incredible transformations. One notable case is that of a young boy named Ethan, who, after just a few months in an ABA program, went from minimal verbal communication to engaging in meaningful conversations with peers and family. He went from “I want cookie” to “May I please have a chocolate chip cookie?”—a true linguistic leap that would make any grammarian proud!Another inspiring example is Sarah, a young girl who struggled with social anxiety.
Through tailored ABA interventions focusing on social interactions, she blossomed! Now, she confidently navigates birthday parties, and her favorite phrase is, “Let’s play hide-and-seek!”—a far cry from her previous “I want to hide!”
Comparison of ABA and Other Therapeutic Approaches
When comparing ABA to other therapeutic approaches for developmental disabilities, it’s essential to grasp the unique strengths each method offers. Here’s a concise overview highlighting the distinctions:
- ABA vs. Speech Therapy: While speech therapy focuses primarily on language development, ABA encompasses a broader range of skills, including social interaction and behavioral modification, allowing for a more holistic approach to development.
- ABA vs. Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy aims at improving daily living skills through physical activities; ABA complements this by reinforcing appropriate behaviors and communication during these activities, creating a well-rounded therapeutic experience.
- ABA vs. Play Therapy: Play therapy engages children in play to address emotional and social issues, whereas ABA utilizes structured techniques to teach specific skills, presenting a more targeted approach to behavioral change.
The combination of these approaches can be effective; however, ABA stands out with its data-driven methods and measurable outcomes. This makes it a go-to choice for many families seeking to unlock the full potential of their loved ones with developmental disabilities.
Integrating ABA with Health Topics

In today’s world, where health and wellness reign supreme, it’s essential to understand how Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) can step into the spotlight and dance its way onto the health stage. With a funky mix of behavioral science and health initiatives, ABA is not just about behavior modification; it can be a superhero for childhood obesity prevention, fitness aspirations, and health condition management.
Grab your capes, folks, as we explore how ABA swoops in to save the day!
ABA Interventions and Childhood Obesity Prevention
The fight against childhood obesity has taken center stage in recent years, making it a sizzling topic that needs our attention. ABA can be integrated into prevention strategies to promote healthier habits among kids. By using a behavior-analytic approach, we can encourage positive changes in diet and physical activity through reinforcement and motivation. This means offering rewards (not just cookies, please!) for choosing fruits over fries or for breaking a sweat rather than breaking the couch.
-
Positive reinforcement works wonders: Praise or rewards for healthy choices can encourage children to stick with them.
- Establishing routines: ABA techniques can help create structured meal times and physical activity sessions, making them feel like more fun than a trip to the amusement park.
- Parent involvement: Training parents on ABA strategies can empower them to model healthy behaviors, turning the household into a mini health boot camp.
Adapting ABA for Fitness and Nutrition Goals
When it comes to fitness and nutrition, ABA can be your trusty sidekick in achieving those glam goals. Whether it’s toning those abs or mastering the art of meal prep, ABA can provide the tools to make those aspirations a reality.
- Setting achievable goals: Breaking down larger fitness or nutrition objectives into smaller, manageable steps helps in maintaining motivation without feeling overwhelmed.
- Tracking progress: Use visual aids like charts or stickers to make tracking progress enjoyable and rewarding, creating a fun competition against yourself.
- Behavior modification strategies: Techniques such as self-monitoring and reinforcement can help individuals stay on track with their meal plans and workout regimens.
ABA’s Role in Managing Health Conditions
ABA’s versatility extends to managing various health conditions, proving itself as a multi-talented player in the game of life. Conditions like asthma, back pain, and depression can benefit significantly from behavioral interventions that focus on changing habits and fostering healthier lifestyles.
- Asthma management: ABA can help establish routines for medication adherence and avoidance of asthma triggers, turning the process into a predictable and manageable behavior.
- Back pain: Encouraging physical therapy attendance and proper body mechanics through behavior modification can help alleviate chronic pain over time.
- Depression: ABA techniques can foster engagement in enjoyable activities, helping to combat lethargy and promote social interaction, which is key in improving mood.
Last Word
In conclusion, ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis) is not just a method; it’s an adventure filled with discoveries about human behavior and the art of change. By utilizing its principles, we can help individuals overcome obstacles, enhance their skills, and live more fulfilling lives. Whether it’s helping a child with autism find their voice or guiding a teenager towards healthier habits, the impact of ABA is profound and far-reaching.
So, next time you see a behavior at play, remember: there’s a whole world of ABA behind it, waiting to unravel its magic!
Questions and Answers
What is the main goal of ABA?
The main goal of ABA is to improve specific behaviors while enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals through systematic interventions.
Is ABA only for individuals with autism?
No, while ABA is widely used for individuals with autism, it can be applied to various populations and settings, including educational and health-related contexts.
How does reinforcement work in ABA?
In ABA, reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors by following them with rewards, making it more likely those behaviors will occur again.
Can ABA be used at home?
Absolutely! ABA techniques can be easily adapted for home settings to help parents encourage positive behaviors in their children.
Are there any ethical concerns with ABA?
Yes, ethical considerations are crucial in ABA, ensuring interventions are respectful, individualized, and aim to promote the well-being of the individual.





